Dementia is commonly associated with older individuals, but it can also affect young adults. In this article, we will explore the causes of dementia in young adults and the various factors that contribute to its development.
By understanding the underlying causes, we can work towards prevention, early detection, and better management of this condition.

Introduction
Dementia is a progressive neurological disorder characterized by a decline in cognitive function, memory loss, and changes in behavior and personality.
While it is often associated with aging, dementia can also occur in young adults, albeit less commonly. Understanding the causes of dementia in this age group is crucial for timely diagnosis and appropriate interventions.
Types of Dementia in Young Adults

Dementia in young adults can be attributed to various underlying conditions. The most common types include:
Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease is a degenerative brain disorder that affects memory, thinking, and behavior. While it typically manifests in older adults, early-onset Alzheimer’s can occur in young adults, usually due to genetic factors.
Vascular Dementia
Vascular dementia results from reduced blood flow to the brain, leading to cognitive decline. Conditions such as stroke, small vessel disease, and blood vessel abnormalities can contribute to vascular young onset dementia.
Frontotemporal Dementia
Frontotemporal dementia primarily affects the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, leading to changes in behavior, personality, and language abilities. It can manifest in young adults due to genetic mutations or family history.
Lewy Body Dementia
Lewy body dementia is characterized by the presence of abnormal protein deposits (Lewy bodies) in the brain. Young adults may develop this type of dementia, which often presents with cognitive fluctuations, visual hallucinations, and movement problems.
Mixed Dementia
Mixed dementia refers to the coexistence of multiple types of dementia, such as Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Young adults may experience mixed dementia due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Genetic Factors
Genetics plays a significant role in the development of dementia, even in young adults. Some specific genetic factors associated with dementia include:
Familial Alzheimer’s Disease
Familial Alzheimer’s disease is a rare form of Alzheimer’s that is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. Young adults with a family history of Alzheimer’s have an increased risk of developing this form of dementia.
Early-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease
Certain genetic mutations can lead to early-onset Alzheimer’s disease, which affects individuals in their 30s, 40s, or 50s. These mutations can be passed down through generations, contributing to young onset dementia.
Genetic Mutations and Their Impact
Other genetic mutations, such as those associated with frontotemporal dementia, Lewy body dementia, and other rare forms of dementia, can also contribute to the development of dementia in young adults.
Environmental Factors
Apart from genetics, environmental factors can also influence the risk of developing dementia in young adults. Some notable factors include:
Head Injuries and Traumatic Brain Injury
Serious head injuries, especially those resulting in brain trauma, have been linked to an increased risk of dementia later in life. Young adults who have suffered significant head injuries may be more susceptible to cognitive decline and dementia.
Substance Abuse and Alcoholism
Long-term substance abuse and alcoholism can have detrimental effects on brain health and cognitive function. Young adults who engage in these behaviors may be at a higher risk of developing dementia.
Infections and Autoimmune Disorders
Certain infections, such as HIV/AIDS, can directly affect the brain and increase the risk of dementia in young adults. Additionally, autoimmune disorders like lupus or multiple sclerosis can contribute to cognitive impairment and dementia.
Medical Conditions
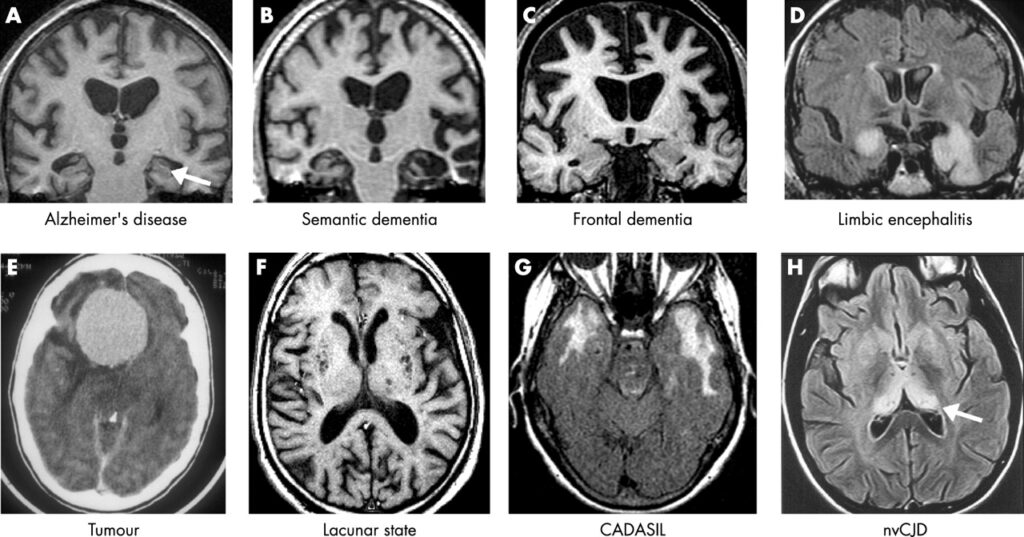
Several medical conditions are associated with an increased risk of young onset dementia. Some examples include:
Down Syndrome
People with Down syndrome have an increased risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease due to the presence of an extra chromosome 21. Young adults with Down syndrome are particularly vulnerable to early-onset dementia.
Huntington’s Disease
Huntington’s disease is a hereditary neurodegenerative disorder that leads to cognitive decline and movement abnormalities. The onset of symptoms can occur during young adulthood and result in dementia over time.
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease is a rare, degenerative brain disorder caused by abnormal proteins called prions. It can manifest in young adults, leading to rapid cognitive decline and dementia.
Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle choices can impact brain health and increase the risk of dementia in young adults. Factors to consider include:
Poor Diet and Lack of Physical Activity
A diet high in saturated fats, refined sugars, and processed foods can contribute to cognitive decline and dementia. Additionally, a sedentary lifestyle without regular exercise can negatively affect brain health.
Chronic Stress and Sleep Deprivation
Excessive stress and chronic sleep deprivation can impair cognitive function and increase the risk of dementia. Young adults who experience prolonged stress or consistently lack quality sleep should be mindful of their long-term brain health.
Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been linked to cognitive decline and an increased risk of dementia. Young adults who engage in these behaviors should be aware of the potential consequences for their brain health.
Cognitive Reserve and Brain Health
Building cognitive reserve through mental stimulation, learning, and social engagement can help protect against the onset of dementia. Young adults can take steps to promote brain health, such as:
Building Cognitive Reserve
Engaging in activities that challenge the brain, such as puzzles, reading, and learning new skills, can help build cognitive reserve. This reserve acts as a buffer against cognitive decline and may delay the onset of dementia.
Promoting Brain Health Through Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and sufficient sleep can significantly contribute to brain health. Young adults should prioritize these lifestyle changes to reduce their risk of dementia.

Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Early detection and diagnosis of young onset dementia are crucial for effective management. Some diagnostic and treatment options include:
Early Detection and Diagnosis
If young adults experience persistent cognitive difficulties or notice changes in their memory, thinking, or behavior, they should seek medical evaluation.
A comprehensive assessment by a healthcare professional can help diagnose the underlying cause of dementia.
Treatment Approaches and Interventions
Treatment for dementia in young adults focuses on managing symptoms, promoting cognitive function, and addressing underlying medical conditions. Medications, cognitive rehabilitation, and therapy may be utilized to improve quality of life.
Supportive Care and Management Strategies
Supportive care, including assistance with daily activities, emotional support, and education for both individuals with dementia and their caregivers, is essential.
Young adults with dementia should explore available resources and support services.
Coping Strategies and Support
Coping with dementia can be challenging for young adults. Various coping strategies and support options are available, including:
Psychological and Emotional Support
Individuals with dementia can benefit from counseling and therapy to address emotional challenges and cognitive changes. Seeking support from mental health professionals can help young adults navigate the emotional impact of the diagnosis.
Support Groups and Counseling
Joining support groups and participating in counseling sessions can provide young adults with dementia a sense of community and understanding. Interacting with others facing similar challenges can be empowering and provide valuable insights.
Financial and Legal Considerations
Young adults with dementia may face unique financial and legal considerations. Engaging with financial advisors and legal professionals early on can help with decision-making, estate planning, and addressing potential future needs.
Research and Future Perspectives
Ongoing research plays a crucial role in understanding the causes of dementia in young adults and developing new treatments. Some aspects to consider include:
Current Studies and Ongoing Research
Scientists and researchers are actively investigating the genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors associated with dementia in young adults. Ongoing studies aim to enhance our understanding of the condition and identify potential interventions.
Potential Advancements in Treatment
Advancements in medical research may lead to new treatment options and interventions for dementia in young adults. Clinical trials and emerging therapies offer hope for improved outcomes and quality of life.
Importance of Raising Awareness
Raising awareness about dementia in young adults is vital to promote early detection, reduce stigma, and ensure appropriate support and resources are available. Education and advocacy efforts can help empower individuals and their families.
Conclusion
Dementia in young adults is a complex condition influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, medical, and lifestyle factors.
By understanding the causes and risk factors associated with dementia, young adults can take proactive steps to protect their brain health.
Early detection, diagnosis, and management strategies, coupled with support and resources, are crucial for improving the quality of life for those affected by dementia.
1. Can dementia occur in young adults?
Yes, dementia can occur in young adults, although it is less common than in older individuals.
Certain types of dementia, such as early-onset Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia, can manifest in young adults, typically due to genetic factors or specific medical conditions.
2. Can you get Alzheimer’s disease in your 20s?
While it is extremely rare, it is possible to develop Alzheimer’s disease in your 20s. This form of early-onset Alzheimer’s, also known as young-onset Alzheimer’s, affects individuals typically between their 30s and 50s.
However, the occurrence of Alzheimer’s disease in this age group is estimated to be less than 5% of all cases. Early-onset Alzheimer’s is often caused by genetic mutations, such as those in the APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2 genes.
Symptoms may include memory loss, confusion, changes in behavior, and difficulties with language and problem-solving.
If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms, it is important to seek medical evaluation for proper diagnosis and management.
3. What are the early signs of dementia in young adults?
The early signs of dementia in young adults may vary depending on the underlying cause.
However, common early symptoms include persistent memory loss, difficulty with problem-solving and decision-making, confusion, changes in behavior and mood, language difficulties, and challenges with completing familiar tasks.
If these symptoms are experienced, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
4. Is dementia in young adults hereditary?
In some cases, dementia in young adults can be hereditary. Certain genetic mutations, such as those associated with familial Alzheimer’s disease and early-onset Alzheimer’s disease, can increase the risk of developing dementia in younger individuals.
However, it is important to note that not all cases of dementia in young adults are hereditary, and other factors, such as environmental and lifestyle factors, can also contribute to its development.
5. How can young adults reduce their risk of developing dementia?
While not all cases of dementia can be prevented, there are steps young adults can take to reduce their risk:
– Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, regular physical exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management.
– Engaging in mentally stimulating activities, such as reading, puzzles, and learning new skills.
– Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
– Managing chronic health conditions, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and obesity.
– Protecting the head from injuries and practicing safety measures to prevent traumatic brain injury.
It is important to remember that these measures may help reduce the risk of dementia but do not guarantee its prevention. Consulting with a healthcare professional for personalized advice is recommended.
6. What resources are available for young adults with dementia?
There are various resources available to support young adults with dementia and their families. Some helpful resources include:
– Alzheimer’s and Dementia Associations: These organizations provide information, support groups, counseling services, and educational materials specifically tailored to young adults with dementia.
– Caregiver Support Services: Caregiver support groups and organizations offer guidance, emotional support, and resources for individuals caring for young adults with dementia.
– Memory Clinics and Neurology Centers: These specialized clinics and centers focus on the diagnosis, treatment, and management of dementia. They often provide comprehensive care and access to clinical trials and research studies.
– Online Communities and Forums: Online platforms and forums dedicated to dementia offer opportunities for young adults and their caregivers to connect with others facing similar challenges, share experiences, and find support.
– Legal and Financial Advisors: Consulting with legal and financial professionals can help young adults with dementia and their families navigate complex matters, such as estate planning, power of attorney, and financial management.
These resources can provide valuable assistance, guidance, and emotional support throughout the journey of living with dementia in young adulthood.