Pain In Abdominal Quadrants: The abdominal cavity is divided into four quadrants for clinical and anatomical reference. The LUQ contains the liver, spleen, stomach, pancreas, and left lobe of the small intestine.
The RUQ contains the right lobe of the liver, the gallbladder, part of the small intestine, and the transverse colon. The LLQ includes the descending colon, part of the small intestine, and in females the left ovary and fallopian tube.
I. Introduction
Abdominal pain is a common complaint encountered in medical practice. It is essential to understand the location of pain within the abdominal quadrants to aid in diagnosing the underlying cause accurately.

This article provides a comprehensive overview of pain in abdominal quadrants, its potential causes, diagnostic approaches, treatment options, and preventive measures.
II. Abdominal Quadrants and Their Organs
The abdominal cavity is divided into four quadrants for clinical reference. The LUQ contains the liver, spleen, stomach, pancreas, and left lobe of the small intestine. The RUQ contains the right lobe of the liver, the gallbladder, part of the small intestine, and the transverse colon.
The LLQ includes the descending colon, part of the small intestine, and in females the left ovary and fallopian tube.
- SIMILAR ARTICLES: What Distinguishes a Heart Attack from Heart Failure?
III. Common Causes of Pain In Abdominal Quadrants

The type of abdominal Quadrant is given below are the part of the abdomen
1. Left Upper Quadrant (LUQ)
Abdominal pain in the left upper quadrant (LUQ) can be attributed to various gastrointestinal causes and conditions related to the spleen. The LUQ is located on the left upper side of the abdomen. LUQ pain can cause to

a. Gastrointestinal causes:
- Gastritis: inflammation of the stomach lining.
- GERD: Chronic acid reflux that causes irritation and inflammation of the esophagus.
b. Conditions related to the spleen:
- Splenic rupture: A tear or rupture in the spleen, often due to trauma or underlying medical conditions.
- Splenomegaly: Enlargement of the spleen usually caused by infections, liver diseases or some cancers.
- Splenic infarction: interruption of blood supply to the spleen, leading to tissue death.
2. Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ)
Abdominal pain in the right upper quadrant (RUQ) is associated with liver-related conditions and problems with the gallbladder. These include:

a. Liver-related conditions:
- Inflammation of the liver is usually caused by viral infections, alcohol abuse, or autoimmune diseases.
- A collection of pus within the liver, typically caused by a bacterial infection.
b. Gallbladder issues:
- Hardened deposits form in the gallbladder, leading to blockage of the bile ducts and causing intense pain.
- Inflammation of the gallbladder is usually caused by gallstones or bacterial infections.
- Biliary colic: Intense pain resulting from the temporary blockage of the bile ducts by gallstones.
3. Left Lower Quadrant (LLQ)
Abdominal pain in the left lower quadrant (LLQ) can be attributed to various intestinal conditions and disorders of the reproductive system. The LLQ is located on the left sided of the abdomen.
a. Intestinal Conditions:
- Diverticulitis: Inflammation or infection of small pouches that develop along the walls of the large intestines.
- Ulcerative colitis: A chronic inflammatory bowel disease characterized by inflammation and ulcers in the colon and rectum.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): A functional gastrointestinal disorder characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits.
b. Reproductive system disorders:
- Ovarian Cysts: Fluid-filled sacs that form on the ovaries that often cause pain if they rupture or twist.
- lumbar region: The tissue that normally lines the uterus grows outside the uterus, leading to pain and swelling.
- PID: An infection of the female reproductive organs, usually caused by sexually transmitted bacteria.
4. Right Lower Quadrant (RLQ)
Abdominal pain in the right lower quadrant (RLQ) is commonly associated with appendicitis and gynecological problems. Besides:

a. Appendicitis:
- Inflammation of the appendix, a small pouch-like structure attached to the beginning of the large intestines. This is a medical emergency that requires immediate surgical removal of the appendix.
b. Gynecological problems:
- Ovarian Torsion: Twisting of the ovary, leading to decreased blood flow and severe pain.
- Ovarian Cyst Rupture: A cyst on the ovary ruptures, causing sudden and sharp pain.
It is important to note that these are general categories and that specific conditions may have additional causes or variations. If experiencing persistent or severe upper abdominal pain, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
- SIMILAR ARTICLES: Hidden Causes of Dementia in Young Adults and Solution in 2023
IV. Diagnostic Approaches for Abdominal Pain

To determine the root cause of abdominal pain, healthcare providers use various diagnostic procedures. These procedures usually include a combination of medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, imaging studies, and special diagnostic procedures.
V. Treatment and Management of Pain In Abdominal Quadrants
Treatment and management of abdominal pain depend on the underlying cause. Here are some common measures for pain relief, specific treatment options for different causes, and lifestyle changes to prevent stomach pain:
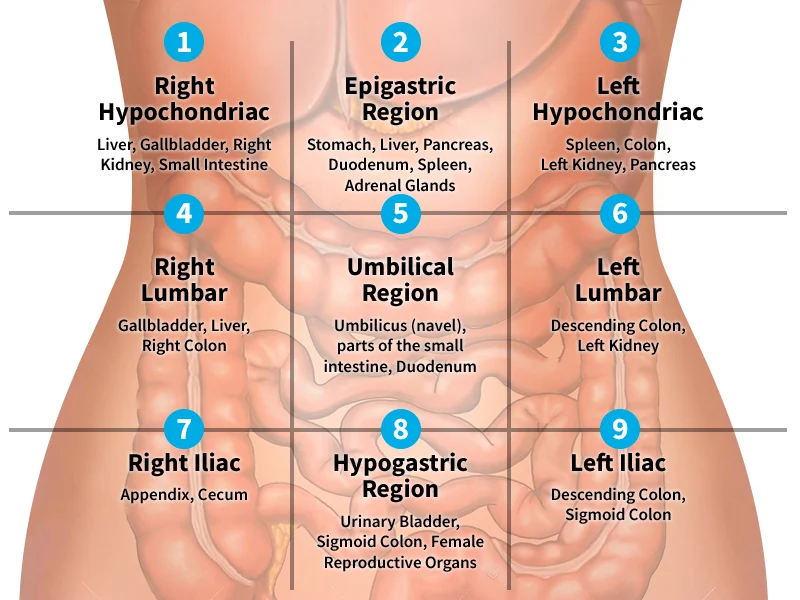
There are 9 abdominal pain locator regions.
1. General measures for pain relief
- Over-the-counter analgesics: Non-prescription pain medications such as ibuprofen can help relieve mild to moderate stomach pain.
- Rest: Resting and allowing the body to rest is beneficial, especially if the pain is associated with physical activity.
2. Specific treatment options for different causes
- Medications: Depending on the underlying cause, specific medications may be prescribed.
- Lifestyle changes: Making changes to one’s diet and lifestyle can be effective in managing some types of stomach pain.
3. Lifestyle changes to prevent abdominal pain
- Balanced Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains promotes good digestion and reduces stomach upset.
- Moderate exercise: Moderate exercise several times a week can help regulate bowel movements and prevent constipation.
- Stress management techniques: Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation or yoga can help manage stress levels. Stress reduction is important because stress can exacerbate abdominal pain in conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome.
4. Type of pain in the stomach- female
Less serious causes of abdominal pain include constipation, irritable bowel syndrome, food allergies, lactose intolerance, food poisoning, and stomach viruses. Other, more serious causes include appendicitis, abdominal aortic aneurysm, bowel obstruction, and cancer.
VI. Tips for Preventing Abdominal Pain
Preventing abdominal pain can be possible with the following tips:
- Maintain a healthy diet: Consuming a balanced diet is essential for good digestive health. Include plenty of fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Avoid or limit fatty, greasy, or spicy foods that cause abdominal discomfort. Stay hydrated by drinking enough water throughout the day.
- Regular Exercise and Physical Activity: Engaging in regular physical activity promotes healthy digestion and prevents stomach aches. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Activities such as walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling can improve bowel function and reduce the risk of conditions such as constipation.
- Stress Management Techniques: Stress and anxiety can contribute to abdominal pain and digestive disturbances. Practice stress management techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies that help you relax.
VII. Conclusion
Abdominal pain can be caused by various reasons and its treatment and management depends on the underlying cause.
It is important to seek medical attention if the pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other related symptoms. However, there are steps you can take to prevent colic.
Remember to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance based on your specific condition and medical history. In case of an emergency, please dial 911 or proceed to the nearest emergency room.
FAQ’s (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. Can stress cause abdominal pain?
Yes, This can disrupt normal digestion and lead to conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or worsen existing digestive problems.
2. What foods should I avoid to prevent abdominal pain?
Foods high in fatty, oily, spicy, or foods that trigger gastrointestinal discomfort should be avoided. This can vary for individuals, but common trigger foods include fatty meats, fried foods, spicy sauces, and carbonated beverages.
3. Is abdominal pain life-threatening?
Abdominal pain can be a symptom of various conditions, some of which can be life-threatening. Examples include appendicitis, ectopic pregnancy, bowel obstruction, or a ruptured organ. It is crucial to seek medical attention if the pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms
4. What causes vomiting blood?
Bleeding in your upper gastrointestinal tract from peptic ulcers or torn blood vessels is a common cause of vomiting blood.
5. Have you been experiencing abdominal pain caused by kidney stones?
Abdominal pain caused by kidney stones Stones pass through the ureter. The pain is often severe and usually in the back or side. Medical evaluation is important for diagnosis and treatment.