Type 2 diabetes is a widespread condition impacting millions of individuals globally. Effective management of this chronic ailment entails a holistic strategy comprising medication, physical activity, and notably, a well-balanced diet. Within the spectrum of dietary considerations for diabetes management, the significance of fruits is paramount. In this article, we’ll delve into “What Fruits Are Good for Type 2 Diabetics,” examining the optimal fruit choices and their beneficial effects on blood sugar levels.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels. According to the latest reports from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 34.2 million people in the United States have diabetes, with around 90-95% of cases being type 2 diabetes.

Role of Diet in Managing Type 2 Diabetes
The role of diet in managing type 2 diabetes cannot be overstated. It serves as a cornerstone in effectively controlling blood sugar levels and mitigating the potential complications linked with diabetes. Making conscientious decisions regarding food intake empowers individuals to take charge of their health outcomes.
Fruits, in particular, emerge as valuable allies in the diabetic diet landscape. They boast a rich nutritional profile, comprising essential vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. What sets fruits apart is their relatively low-calorie content and glycemic index. This means that they provide valuable nutrients without causing significant spikes in blood sugar levels, which is crucial for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
By incorporating fruits into their daily diet, individuals with type 2 diabetes can enjoy a wide array of health benefits. These include improved glycemic control, better weight management, and reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, the diverse range of flavors and textures offered by fruits makes them a versatile and enjoyable component of any meal plan.
In essence, fruits serve as an excellent dietary option for individuals managing type 2 diabetes. Their nutritional density, coupled with their low glycemic impact, makes them an indispensable part of a balanced and diabetes-friendly diet.
Nutritional Benefits of Fruits for Type 2 Diabetics
Fruits are packed with essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants, which are all crucial for maintaining good health and well-being. For individuals with type 2 diabetes, adding fruits to their diet can have several benefits. These include better control over blood sugar levels, reduced inflammation in the body, and a decreased risk of heart disease. Essentially, consuming fruits provides diabetic individuals with a natural and nutritious way to manage their condition and promote overall health.
What Fruits Are Good for Type 2 Diabetics
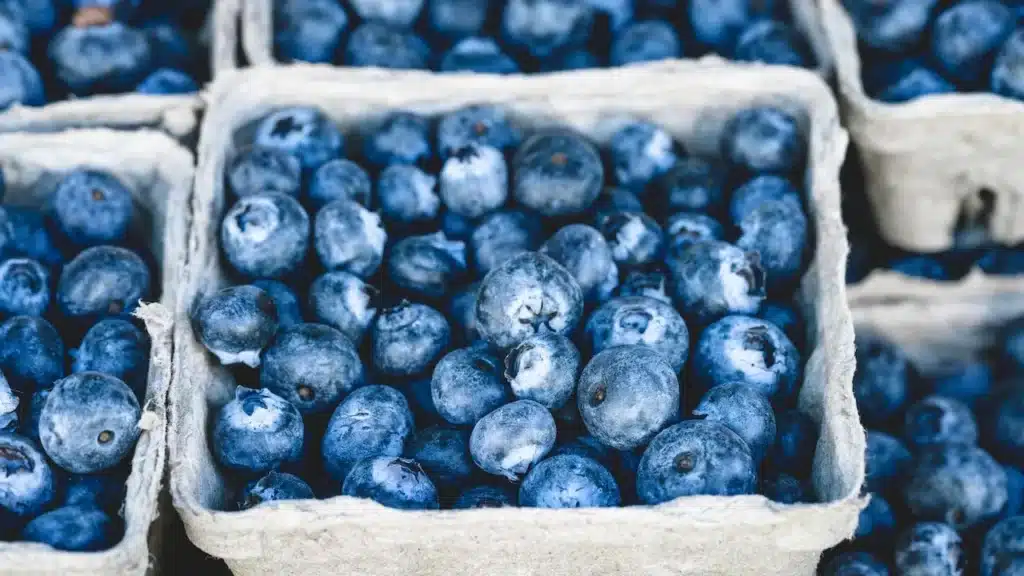

a. Berries
why berries are considered the best fruit for individuals with type 2 diabetes, presented in points with supporting evidence:
- Rich in Antioxidants: Berries, such as strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries, are packed with antioxidants like anthocyanins and flavonoids. These compounds help combat oxidative stress and inflammation, which are key factors in developing and progressing type 2 diabetes. (Source: “Antioxidants in Berries and Their Impact on Human Health” – Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry)
- High in Fiber: Berries are an excellent source of dietary fiber, including both soluble and insoluble fiber. Fiber helps slow down the absorption of sugars in the bloodstream, preventing rapid spikes in blood sugar levels after meals. This can aid in better glycemic control for individuals with type 2 diabetes. (Source: “Dietary Fiber Intake and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus” – Archives of Internal Medicine)
- Improves Insulin Sensitivity: Research studies have demonstrated that regular consumption of berries can improve insulin sensitivity in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Insulin sensitivity refers to the ability of cells to respond effectively to insulin and uptake glucose from the bloodstream. Improved insulin sensitivity helps regulate blood sugar levels more efficiently. (Source: “Berries: Anti-inflammatory Effects in Humans” – Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry)
- Low Glycemic Index: Berries generally have a low glycemic index (GI), meaning they cause a gradual and modest increase in blood sugar levels compared to high-GI foods. Foods with a low GI are preferred for individuals with diabetes as they help maintain more stable blood sugar levels. (Source: “International Tables of Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load Values” – Diabetes Care)
- Weight Management: Berries are relatively low in calories and can be incorporated into a balanced diet for weight management, which is crucial for individuals with type 2 diabetes. The high fiber content in berries also promotes satiety, helping individuals feel fuller for longer and potentially reducing overall calorie intake. (Source: “Effects of Berry Consumption on Body Composition and Metabolic Health” – Nutrients)
In summary, berries are considered the best fruit for individuals with type 2 diabetes due to their rich antioxidant content, high fiber content, ability to improve insulin sensitivity, low glycemic index, and potential benefits for weight management. These factors make berries an excellent choice for supporting overall health and managing blood sugar levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
b. Citrus fruits
Explaining the suitability of citrus fruits for individuals with type 2 diabetes:

- High Vitamin C Content: Citrus fruits, including oranges, grapefruits, and lemons, are rich in vitamin C. This essential nutrient is crucial in supporting the immune system and overall health. For individuals with type 2 diabetes, maintaining a strong immune system is important for preventing infections and other complications. (Source: “Vitamin C and Immune Function” – Nutrients)
- Low Glycemic Index: Citrus fruits have a low glycemic index (GI), meaning they cause a gradual and modest increase in blood sugar levels compared to high-GI foods. This property makes them suitable for individuals with diabetes as they help prevent rapid spikes in blood sugar levels after consumption. (Source: “Glycemic Index of Different Fruits” – Journal of the American Dietetic Association)
- Cholesterol-Lowering Effects: Some studies suggest that citrus fruits may help lower cholesterol levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes. High cholesterol is a common concern for individuals with diabetes as it increases the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular complications. By incorporating citrus fruits into their diet, individuals may experience improvements in their lipid profile, contributing to better heart health. (Source: “Citrus Flavonoids as Regulators of Lipoprotein Metabolism and Atherosclerosis” – Nutrients)
- Improves Insulin Resistance: Research indicates that certain compounds found in citrus fruits, such as flavonoids and polyphenols, may help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce insulin resistance in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Improved insulin sensitivity allows cells to more effectively respond to insulin and uptake glucose from the bloodstream, leading to better blood sugar control. (Source: “Flavonoids and Insulin Resistance” – Molecular Nutrition & Food Research)
In summary, citrus fruits like oranges, grapefruits, and lemons are excellent choices for individuals with type 2 diabetes due to their high vitamin C content, low glycemic index, potential cholesterol-lowering effects, and ability to improve insulin resistance. Including citrus fruits as part of a balanced diet can contribute to better overall health and blood sugar management for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
c. Apples:
Explaining the benefits of apples for individuals with type 2 diabetes:

- Soluble Fiber Content: Apples are rich in soluble fiber, which plays a key role in promoting digestive health and blood sugar management. Soluble fiber helps slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, preventing rapid spikes in blood glucose levels after meals. This can aid in better glycemic control for individuals with type 2 diabetes. (Source: “Dietary Fiber and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus” – JAMA Internal Medicine)
- Promotes Satiety: The fiber content in apples also promotes a feeling of fullness or satiety, which can help individuals with type 2 diabetes manage their weight more effectively. By reducing feelings of hunger and preventing overeating, including apples in the diet can support weight loss efforts, which is important for managing diabetes and reducing the risk of complications. (Source: “Effects of Apple Consumption on Metabolic Health and Weight Management” – Nutrients)
- Blood Sugar Management: Consuming apples as part of a balanced diet can contribute to better blood sugar management for individuals with type 2 diabetes. The combination of soluble fiber and natural sugars in apples helps regulate blood glucose levels, preventing sudden spikes and crashes. This can lead to more stable energy levels throughout the day and improved overall health. (Source: “Apple Intake and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes” – American Journal of Clinical Nutrition)
- Weight Loss Support: Apples are a low-calorie, nutrient-dense food that can be included in a weight loss diet for individuals with type 2 diabetes. By providing essential nutrients and fiber while being relatively low in calories, apples can help individuals achieve and maintain a healthy weight, which is important for managing diabetes and reducing the risk of complications. (Source: “Role of Fruits and Vegetables in Weight Management” – Nutrition Reviews)
In summary, including apples in the diet of individuals with type 2 diabetes can have several benefits, including improved blood sugar management, support for weight loss efforts, and promotion of overall health and well-being. The soluble fiber content in apples plays a particularly important role in these benefits, making them a valuable addition to a diabetic-friendly diet.
d. Pears:
Explaining why pears are a beneficial choice for individuals with type 2 diabetes:
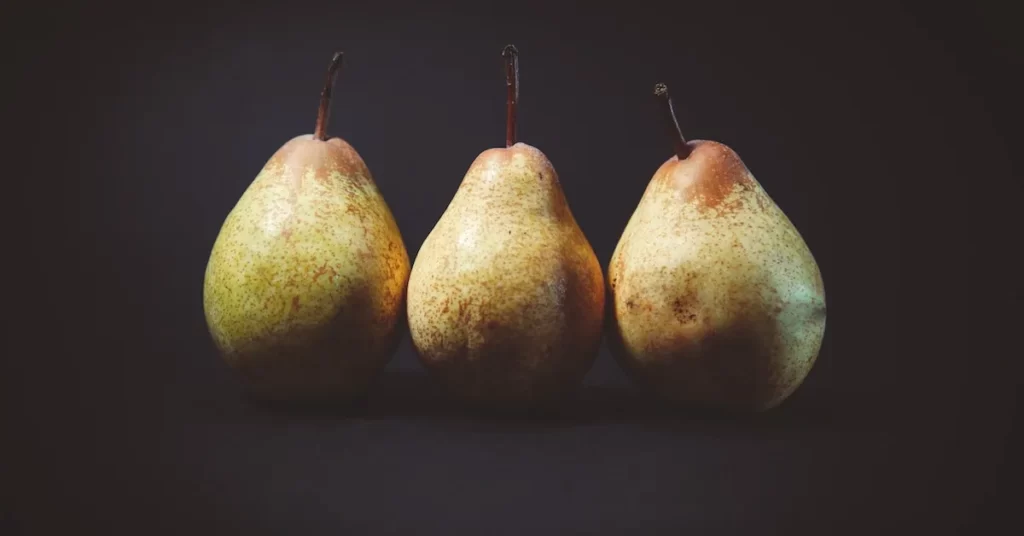

- High Fiber Content: Pears are rich in dietary fiber, which is beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Fiber helps slow down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, preventing rapid spikes in blood sugar levels after meals. This can aid in better glycemic control and overall blood sugar management. (Source: “Dietary Fiber Intake and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus” – Archives of Internal Medicine)
- Low Glycemic Index: Pears have a low glycemic index (GI), meaning they cause a gradual and modest increase in blood sugar levels compared to high-GI foods. Foods with a low GI are preferred for individuals with diabetes as they help maintain more stable blood sugar levels. Consuming pears as part of a balanced diet can help prevent sudden spikes and crashes in blood glucose levels. (Source: “Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load Values of Foods: 2008” – Diabetes Care)
- Sustained Energy: The combination of fiber and natural sugars in pears provides a source of sustained energy, making them an ideal snack option for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Unlike foods high in refined sugars, which can cause rapid fluctuations in blood sugar levels, pears provide a steady release of energy without the risk of spiking blood glucose levels. (Source: “The Role of Dietary Fiber in Diabetes Management” – Current Diabetes Reports)
- Promotes Digestive Health: The high fiber content in pears also promotes digestive health by supporting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Maintaining good digestive health is important for individuals with type 2 diabetes, as it can help optimize nutrient absorption and overall well-being. Including pears in the diet can contribute to a healthy digestive system and better overall health outcomes. (Source: “Dietary Fiber and Digestive Health” – Nutrition Reviews)
In summary, pears are an excellent fruit choice for individuals with type 2 diabetes due to their high fiber content, low glycemic index, ability to provide sustained energy, and promotion of digestive health. Including pears in the diet as part of a balanced meal plan can help individuals with diabetes better manage their blood sugar levels and improve overall health.
e. Cherries
Explaining the benefits of cherries for individuals with type 2 diabetes:

- Rich in Antioxidants and Anti-inflammatory Compounds: Cherries, whether sweet or tart, are packed with antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds. These bioactive compounds help combat oxidative stress and inflammation, which are key factors in developing and progressing type 2 diabetes and its complications. (Source: “Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Properties of Cherries” – Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry)
- Potential Blood Sugar Lowering Effects: Research suggests that cherries may have blood sugar-lowering effects, making them beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Some studies have found that consuming cherries or cherry extract can lead to reductions in fasting blood sugar levels and improvements in insulin sensitivity. (Source: “Effects of Cherry Consumption on Glycemic Control and Insulin Sensitivity” – Nutrients)
- Reduces Risk of Diabetes-related Complications: Cherries have been shown to reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications such as neuropathy and retinopathy. The antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds in cherries help protect against nerve damage and vision problems commonly associated with diabetes. Including cherries in the diet may help individuals with type 2 diabetes reduce their risk of these complications. (Source: “Cherry Consumption and Risk of Diabetes-related Complications” – Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry)
- Low Glycemic Index: Cherries have a relatively low glycemic index (GI), meaning they cause a gradual and modest increase in blood sugar levels compared to high-GI foods. Foods with a low GI are preferred for individuals with diabetes as they help maintain more stable blood sugar levels. Consuming cherries as part of a balanced diet can help prevent sudden spikes and crashes in blood glucose levels. (Source: “Glycemic Index of Various Cherry Varieties” – Journal of Food Science)
In summary, cherries are a beneficial fruit choice for individuals with type 2 diabetes due to their high antioxidant and anti-inflammatory content, potential blood sugar-lowering effects, ability to reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications, and low glycemic index. Including cherries in the diet can contribute to better blood sugar control and overall health for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
f. Grapes
Explaining the considerations for individuals with type 2 diabetes regarding grapes:

- Nutrient-Rich Profile: Grapes contain natural sugars, but they also offer a variety of health-promoting compounds such as resveratrol and quercetin. These bioactive compounds have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, which are beneficial for overall health and may help protect against chronic diseases. (Source: “Health Benefits of Grapes: Polyphenols and Beyond” – Nutrients)
- Moderation is Key: While grapes can be enjoyed as part of a balanced diet, individuals with type 2 diabetes should consume them in moderation. Despite their nutritional benefits, grapes still contain sugars that can affect blood sugar levels. Therefore, individuals with diabetes need to monitor their portion sizes and overall carbohydrate intake when including grapes in their diet. (Source: “Dietary Carbohydrate Intake and Blood Glucose Control in Type 2 Diabetes” – Nutrition Reviews)
- Resveratrol Content: Grapes, especially red and purple varieties, are rich in resveratrol, a polyphenol compound known for its potential health benefits. Research suggests that resveratrol may have positive effects on blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity, making it potentially beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes. However, more studies are needed to fully understand the effects of resveratrol on diabetes management. (Source: “Resveratrol and Diabetes: From Animal to Human Studies” – Biochimica et Biophysica Acta)
- Quercetin Content: Grapes also contain quercetin, another polyphenol compound with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Quercetin may help improve cardiovascular health, reduce inflammation, and enhance insulin sensitivity, all of which are important considerations for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Including grapes in the diet can provide a source of quercetin along with other essential nutrients. (Source: “Quercetin: A Versatile Flavonoid” – Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology)
In summary, grapes can be enjoyed in moderation as part of a balanced diet for individuals with type 2 diabetes. While they contain natural sugars, grapes also offer a range of health-promoting compounds like resveratrol and quercetin, which may have benefits for diabetes management and overall health. By monitoring portion sizes and overall carbohydrate intake, individuals with diabetes can include grapes as a nutritious addition to their diet.
g. Watermelon
Discussing the suitability of watermelon for individuals with type 2 diabetes:
- Low Glycemic Index: Despite its sweet taste, watermelon has a relatively low glycemic index (GI), meaning it causes a gradual and modest increase in blood sugar levels compared to high-GI foods. This property makes it a suitable option for individuals with diabetes when consumed in moderation. Watermelon’s low GI helps prevent rapid spikes in blood glucose levels, contributing to better glycemic control. (Source: “Glycemic Index of Watermelon” – European Journal of Clinical Nutrition)
- Hydration: Watermelon is composed primarily of water, making it a hydrating fruit option. Staying hydrated is important for individuals with diabetes to support overall health and well-being. Adequate hydration helps regulate body temperature, maintain electrolyte balance, and support proper kidney function, all of which are essential for individuals managing diabetes. (Source: “Hydration in Diabetes” – Diabetes Spectrum)
- Rich in Vitamins: Watermelon is rich in essential vitamins, particularly vitamin A and vitamin C. These vitamins play important roles in maintaining overall health and supporting immune function. Vitamin A is essential for vision health, while vitamin C is an antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Including watermelon in the diet provides a natural source of these vitamins, contributing to overall health and well-being. (Source: “Vitamins and Minerals in Diabetes” – Journal of Clinical Medicine)
- Moderation is Key: While watermelon can be enjoyed by individuals with diabetes, moderation is key. Despite its low glycemic index, watermelon still contains natural sugars that can affect blood sugar levels. Therefore, individuals with diabetes need to monitor their portion sizes and overall carbohydrate intake when consuming watermelon. Including watermelon as part of a balanced diet can provide hydration and essential nutrients without negatively impacting blood sugar control. (Source: “Dietary Guidelines for Diabetes” – Diabetes Care)
In summary, watermelon can be a suitable fruit option for individuals with type 2 diabetes when consumed in moderation. With its low glycemic index, hydrating properties, and richness in essential vitamins, watermelon can be a refreshing and nutritious addition to a diabetic-friendly diet. By practicing moderation and monitoring portion sizes, individuals with diabetes can enjoy the benefits of watermelon while maintaining good blood sugar control.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding “What Fruits Are Good for Type 2 Diabetics” is crucial for managing this condition effectively. Fruits play a vital role in a diabetic-friendly diet, offering a plethora of nutrients while helping to regulate blood sugar levels.
By selecting fruits with a low glycemic index and incorporating them into meals and snacks, individuals with type 2 diabetes can enjoy a diverse array of flavors while supporting better blood sugar control and overall health. With their rich nutritional profiles and various health benefits, fruits serve as indispensable allies in the management of type 2 diabetes. By making mindful choices and practicing moderation, individuals can harness the power of fruits to enhance their well-being and thrive despite their condition.