In the realm of neuroscience, the intricate workings of the human brain continue to astound and captivate researchers. Recent advancements in mapping stress neurons have shed light on the fascinating connection between stress and estrogen.
This groundbreaking research has unraveled a new dimension in understanding how hormones influence our mental and emotional well-being. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of stress neurons, their mapping in the brain, and the profound link they share with estrogen.
So, let’s embark on this journey of exploration and unravel the mysteries of the brain.
1. Introduction: Unveiling the Stress Brain Connection
The human brain is a labyrinthine organ that houses billions of neurons responsible for orchestrating our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. It is no surprise that stress, a prevalent aspect of our lives, profoundly impacts our brain function.
Recent advancements in neuroscience have uncovered stress neurons, specialized cells that respond to stressors and modulate our physiological and emotional responses.
Understanding the intricate connection between stress and the brain is crucial in comprehending how we perceive, process, and cope with stressful situations.
2. The Neurobiology of Stress Neurons
Stress neurons, also known as stress-responsive neurons or stress-sensitive neurons, are a subset of neurons that are highly responsive to stress signals.
These neurons are primarily located in specific regions of the brain, such as the hypothalamus and the amygdala, which are key players in regulating the stress response.
When exposed to stress, these neurons become activated and initiate a cascade of neurochemical events that prepare the body for a fight-or-flight response.
3. The Mapping of Stress Neurons
Advancements in neuroimaging techniques have enabled researchers to map the activity of stress neurons in the brain with greater precision.
By utilizing cutting-edge technologies like functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET), scientists have been able to identify the regions of the brain that exhibit heightened neural activity during stress.
These advancements have provided valuable insights into the brain’s intricate network and how stress is processed and perceived.
Estrogen Definition:
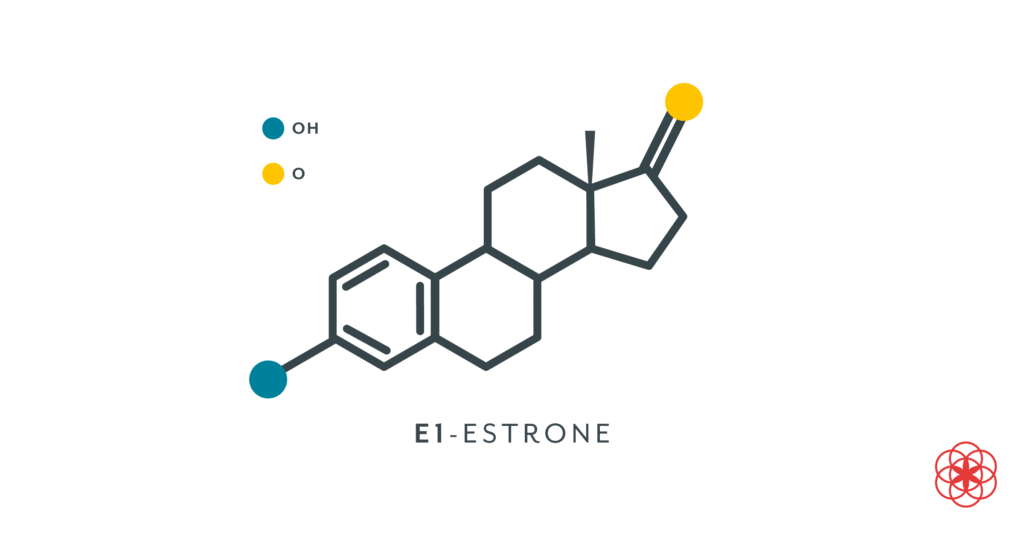
Estrogen meaning to a group of hormones that play a vital role in the development and functioning of the female reproductive system.
These hormones are primarily produced in the ovaries, although smaller amounts are also produced in the adrenal glands and fat tissues.
Estrogen is responsible for the development of secondary sexual characteristics in females, including breast growth, widening of hips, and the onset of menstruation. It also regulates the menstrual cycle and is involved in the maintenance of bone health.
Estrogen Influence on Stress Neurons: Unraveling the Link
Estrogen, a prominent hormone in the female reproductive system, has long been associated with various physiological processes. However, emerging research has highlighted its role in modulating the stress response.
Studies have revealed that estrogen receptors are abundantly present in stress-responsive brain regions, suggesting a significant interaction between estrogen and stress neurons.
This newfound connection has sparked curiosity and opened avenues for further investigation into the complex interplay between hormones and stress.
Estrogen and Mental Health: A Complex Interplay
The influence of estrogen extends beyond its reproductive functions. It plays a crucial role in mental health and emotional well-being. Fluctuations in estrogen levels, such as those experienced during the menstrual cycle or menopause, can impact mood, cognition, and overall mental state.
Understanding the intricate relationship between estrogen and stress is vital in comprehending the gender disparities observed in stress-related disorders.
Hidden Causes of Dementia in Young Adults and Solution in 2023
Impact of Estrogen on Stress Perception
Research suggests that estrogen influences the perception and appraisal of stressors. It can modulate the brain’s response to stress, altering the release of stress hormones and neurotransmitters.
Estrogen has been found to enhance resilience to stress in some individuals, while in others, it may exacerbate stress-related symptoms.
Unraveling the mechanisms behind these divergent responses holds great potential in developing personalized interventions for stress management.
Estrogen’s Influence on Emotional Resilience
Emotional resilience, the ability to bounce back from stressful experiences, is a key factor in maintaining mental well-being. Estrogen has been shown to impact emotional resilience by interacting with neurotransmitter systems involved in mood regulation, such as serotonin and dopamine.
Understanding how estrogen influences these systems can provide valuable insights into developing targeted therapeutic approaches for individuals struggling with stress-related emotional disturbances.
Understanding Estrogen Receptors in the Brain
Estrogen exerts its effects by binding to specific receptors located in different brain regions. These receptors, known as estrogen receptors alpha (ERα) and beta (ERβ), are widely distributed in stress-responsive areas, including the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex.
By deciphering the role of these receptors in stress modulation, researchers aim to unravel the intricate mechanisms underlying the estrogen-stress connection.
7 Stages of Dementia Before Death: Symptoms, Progression & Durations
Estrogen and Neurotransmitter Regulation
Neurotransmitters, chemical messengers in the brain, play a pivotal role in stress regulation. Estrogen has been found to modulate the release and reuptake of neurotransmitters, thereby influencing the communication between brain cells.
By investigating the interplay between estrogen and neurotransmitter systems, scientists aim to gain a comprehensive understanding of how estrogen contributes to stress-related neurochemical changes.
The Role of Estrogen in Neural Plasticity
Neural plasticity, the brain’s ability to reorganize and form new connections, is crucial for adaptation and learning. Estrogen has been shown to influence synaptic plasticity, neuronal growth, and the formation of new neurons in stress-related brain regions.
Unraveling the mechanisms underlying estrogen’s role in neural plasticity can provide valuable insights into the development of therapeutic interventions for stress-related disorders.
Estrogen and Stress-Related Disorders
Stress-related disorders, such as anxiety disorders and depression, disproportionately affect women. The influence of estrogen on stress perception and stress response may contribute to these gender disparities.
Understanding how estrogen interacts with the neural circuits involved in stress-related disorders can pave the way for novel approaches to their prevention and treatment.
Exploring Estrogen Therapies for Stress Management
The potential therapeutic implications of estrogen in stress management have gained considerable attention. Researchers are exploring the use of hormone replacement therapies and selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) to regulate estrogen levels and alleviate stress-related symptoms.
However, the complexities surrounding estrogen’s effects necessitate further research to ensure safe and effective interventions.
Strategies to Naturally Regulate Estrogen Levels
For individuals seeking natural ways to regulate estrogen levels and manage stress, various lifestyle modifications can be beneficial.
Regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in phytoestrogens, stress-reducing practices like meditation and mindfulness, and adequate sleep has been shown to have positive effects on estrogen regulation and stress resilience.
The Future of Estrogen Research
As the intricate relationship between estrogen and stress continues to unfold, the future of estrogen research appears promising. Advancements in neuroimaging, molecular biology, and genetics offer unprecedented opportunities to unravel the complexities of the brain and its interaction with hormones. This knowledge will not only deepen our understanding of stress but also pave the way for personalized interventions targeting stress-related disorders.
Side Effects of Estrogen:
While estrogen plays a crucial role in the female body, there are potential side effects associated with its use or fluctuations in its levels. It is important to note that side effects can vary depending on the specific estrogen treatment or condition. Here are some commonly reported side effects:
- Menstrual Irregularities: Estrogen levels can impact the regularity of the menstrual cycle. Some individuals may experience irregular or heavier periods.
- Breast Tenderness: Estrogen can cause breast tenderness or sensitivity. This side effect is usually temporary and subsides over time.
- Nausea: Some individuals may experience nausea, especially when starting estrogen treatment. Taking the medication with food or adjusting the dosage can help alleviate this side effect.
- Headaches: Estrogen can trigger headaches or migraines in some individuals. Managing stress, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and adjusting the medication if necessary can help manage this side effect.
- Mood Changes: Fluctuations in estrogen levels can affect mood and emotional well-being. Some individuals may experience mood swings, irritability, or increased anxiety. It is important to monitor any significant changes and discuss them with a healthcare provider.
- Weight Changes: Estrogen can influence body weight and the distribution of fat. Some individuals may experience weight gain or changes in body composition.
- Bloating: Estrogen can contribute to water retention and bloating in some individuals. Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet can help alleviate this side effect.
- Blood Clotting: Estrogen has the potential to increase the risk of blood clots, especially in individuals with underlying conditions or risk factors. It is important to discuss any personal or family history of blood clotting disorders with a healthcare provider.
- Breast Cancer Risk: Prolonged exposure to high levels of estrogen, particularly without the balance of progesterone, can increase the risk of certain types of breast cancer. Regular breast examinations and mammograms are essential for monitoring breast health.
It is crucial to remember that the benefits and risks of estrogen treatment or fluctuations in estrogen levels should be evaluated on an individual basis. Working closely with a healthcare provider can help manage potential side effects and optimize the use of estrogen for specific medical conditions or hormonal imbalances.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the mapping of stress neurons in the brain has provided remarkable insights into the profound connection between stress and estrogen. Estrogen, a hormone traditionally associated with reproductive functions, is now recognized as a key player in stress modulation. By unraveling the intricate mechanisms underlying this interaction, researchers are paving the way for innovative approaches to stress management and the prevention of stress-related disorders.
1. How do stress neurons respond to different stressors?
A. Stress neurons are highly responsive to various stressors, including physical, psychological, and environmental stimuli. They become activated and initiate a cascade of neurochemical events that prepare the body for a fight-or-flight response.
2. Can estrogen levels affect stress perception?
A. Yes, estrogen levels have been found to influence stress perception. Fluctuations in estrogen levels can modulate the brain’s response to stress and alter the release of stress hormones and neurotransmitters.
3. Are there natural ways to regulate estrogen levels and manage stress?
A. Yes, lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress-reducing practices like meditation, and adequate sleep can help regulate estrogen levels and enhance stress resilience.
4. What are the potential therapeutic implications of estrogen in stress management?
A. Estrogen replacement therapies and selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) are being explored as potential interventions for stress management. However, further research is needed to ensure their safety and efficacy.
5. How does estrogen influence emotional resilience?
A. Estrogen interacts with neurotransmitter systems involved in mood regulation, influencing emotional resilience. It can modulate the release and reuptake of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine.
